The very term continues to stimulate admiration, envy, and in the hearts of numerous public business CEOs fear. In current years, private equity firms have filched huge and controversial sums, while stalking ever bigger acquisition targets. Certainly, the global worth of private equity buyouts bigger than $1 billion grew from $28 billion in 2000 to $502 billion in 2006, according to Dealogic, a firm that tracks acquisitions.

Private equity firms’ reputation for considerably increasing the value of their investments has actually assisted sustain this development. Their capability to achieve high returns is generally attributed to a variety of factors: high-powered incentives both for private equity portfolio managers and for the operating managers of organisations in the portfolio; the aggressive use of financial obligation, which supplies financing and tax benefits; an identified concentrate on cash flow and margin improvement; and flexibility from restrictive public company guidelines. tyler tysdal business.

That method, which embodies a combination of business and investment-portfolio management, is at the core of private equity’s success. Public companieswhich invariably get companies with the objective of holding on to them and integrating them into their operationscan successfully discover or borrow from this buy-to-sell technique. To do so, they first need to understand simply how private equity companies utilize it so effectively.

It does not make good sense when an acquired service will gain from crucial synergies with the buyer’s existing portfolio of services. It certainly isn’t the way for a business to profit from an acquisition whose primary appeal is its potential customers for long-lasting natural development. However, as private equity companies have revealed, the strategy is ideally suited when, in order to understand an onetime, brief- to medium-term value-creation opportunity, buyers should take outright ownership and control.

It can also be found with businesses that are undervalued because their potential isn’t easily apparent. In those cases, as soon as the changes necessary to accomplish the uplift in worth have been madeusually over a period of 2 to 6 yearsit makes sense for the owner to offer business and carry on to brand-new opportunities.

Specific funds can have their own timelines, financial investment objectives, and management viewpoints that separate them from other funds held within the very same, overarching management firm. Successful private equity firms will raise numerous funds over their lifetime, and as firms grow in size and complexity, their funds can grow in frequency, scale and even specificity. For more information about business partner and - check out the websites and -.
Prior to establishing Freedom Factory, Tyler Tysdal managed a development equity fund in association with numerous celebs in sports and home entertainment. Portfolio business Leesa.com grew quickly to over $100 million in earnings and has a visionary social objective to “end bedlessness” by contributing one mattress for every single 10 offered, with over 35,000 donations now made. Some other portfolio business were in the industries of wine importing, specialty lending and software-as-services digital signage. In parallel to managing assets for businesses, Tyler Tysdal was handling personal equity in real estate. He has had a variety of successful private equity financial investments and a number of exits in student housing, multi-unit real estate, and hotels in Manhattan and Seattle.
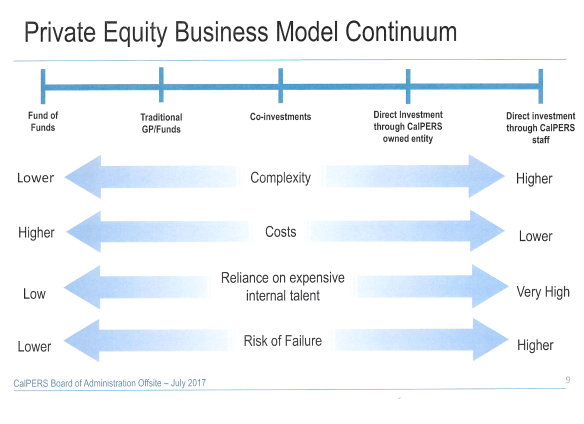
Private equity firms raise funds from institutions and wealthy individuals and after that invest that money in purchasing and selling companies. After raising a defined quantity, a fund will near brand-new investors; each fund is liquidated, offering all its services, within a preset time frame, typically no greater than 10 years. private equity fund.
Private equity companies accept some restrictions on their usage of investors’ money. A fund management contract may restrict, for instance, the size of any single service financial investment. When money is dedicated, however, investorsin contrast to investors in a public companyhave practically no control over management (tysdal lone tree). Although many firms have a financier advisory council, it has far less powers than a public company’s board of directors.
Private Equity Definition, Companies, Pros & Cons – Gocardless
Instead, private equity firms exercise control over portfolio companies through their representation on the business’ boards of directors. Normally, private equity companies ask the CEO and other leading operating managers of an organisation in their portfolios to personally buy it as a method to ensure their dedication and motivation.
In accordance with this model, operating supervisors in portfolio organisations usually have greater autonomy than unit managers in a public company. Although private equity companies are starting to develop operating abilities of their own and hence are now most likely to take an active function in the management of a gotten business, the standard model in which private equity owners supply advice but do not intervene straight in everyday operations still dominates.
Fund revenues are mostly realized through capital gains on the sale of portfolio companies. Due to the fact that financing acquisitions with high levels of debt improves returns and covers private equity companies’ high management fees, buyout funds look for out acquisitions for which high financial obligation makes good sense. state prosecutors mislead. To ensure they can pay funding expenses, they search for steady cash flows, restricted capital expense requirements, at least modest future growth, and, above all, the chance to enhance performance in the brief to medium term.

In some countriesparticularly the United Statesthat provides crucial tax and regulative benefits over public companies. The advantages of purchasing to sell in such situations are plainthough, once again, often ignored. Think about an acquisition that quickly increases in valuegenerating a yearly financier return of, state, 25% a year for the very first three yearsbut subsequently makes a more modest if still healthy return of, say, 12% a year.
A varied public company that attains identical operational efficiency with the obtained businessbut, as is common, has purchased it as a long-lasting investmentwill make a return that gets closer to 12% the longer it owns business. For the public business, holding on to the business once the value-creating changes have been made waters down the final return.
Under their previous owners, those services had often struggled with disregard, inappropriate performance targets, or other restrictions. Even if well managed, such services may have did not have an independent performance history due to the fact that the parent business had integrated their operations with those of other units, making the businesses hard to worth. Sales by public companies of unwanted company systems were the most essential classification of big private equity buyouts till 2004, according to Dealogic, and the prominent companies’ extensively appreciated history of high financial investment returns comes mainly from acquisitions of this type.
( See the exhibit “Private Equity’s New Focus.”) This has actually created new difficulties for private equity firms. In public business, easily understood improvements in performance typically have currently been attained through better corporate governance or the activism of hedge funds. For example, a hedge fund with a considerable stake in a public business can, without needing to buy the company outright, pressure the board into making valuable modifications such as selling unnecessary properties or spinning off a noncore unit.
Why Private Equity Firms Are Reaching Out To Specialized
When KKR and GS Capital Partners, the private equity arm of Goldman Sachs, obtained the Wincor Nixdorf unit from Siemens in 1999, they had the ability to work with the incumbent management and follow its plan to grow revenues and margins. In contrast, given that taking Toys “R” United States private in 2005, KKR, Bain Capital, and Vornado Realty Trust have actually needed to replace the whole leading management team and establish a whole brand-new technique for business.
And it might end up being harder for companies to squander of their investments by taking them public; offered the present high volume of buyouts, the number of big IPOs could strain the stock markets’ ability to absorb brand-new concerns in a few years. Even if the existing private equity financial investment wave recedes, though, the distinct advantages of the buy-to-sell approachand the lessons it uses public companieswill remain – investors state prosecutors.
In contrast, a service unit that has been part of a public business’s portfolio for some time and has carried out adequately, if not amazingly, typically doesn’t get concern attention from senior management. In addition, due to the fact that every investment made by a private equity fund in a company must be liquidated within the life of the fund, it is possible to specifically measure money returns on those investments (civil penalty $).